In an animal experiment modeled on type I diabetic rats, the researchers found that LIPUS had a significant effect on the improvement of penile erectile function
LIPUS can reverse the pathological changes of penile tissue in experimental animals

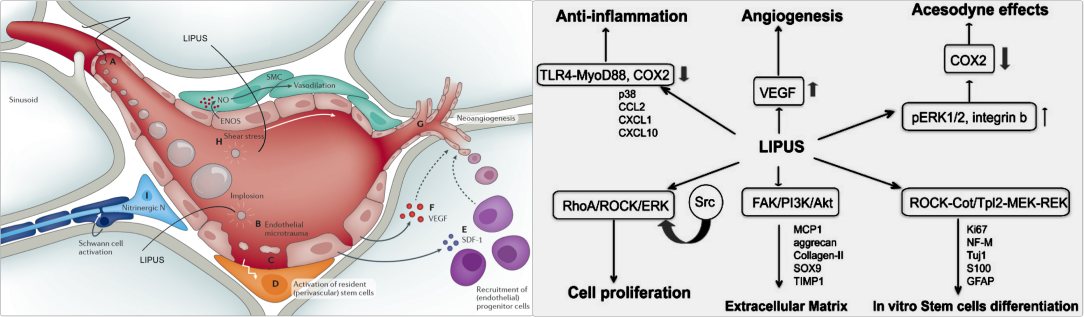
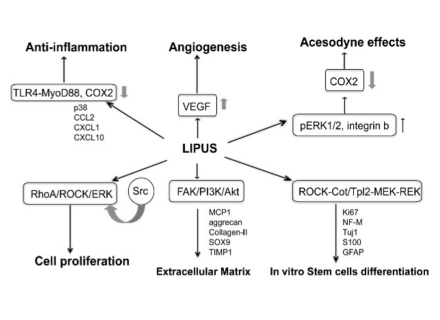
Research progress on the mechanical force biological chain endogenous stem cell activation for the treatment of erectile dysfunction Mechanical force for the treatment of ED Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS): Ultrasound, as a form of mechanical vibration transmission, can continuously propagate horizontally or vertically in elastic media, and has good directionality and strong penetration. Ultrasound has a variety of biophysical effects, including thermal effect, mechanical effect and cavitation effect.
Thermal effect refers to the conversion of mechanical energy of ultrasound through tissue into thermal energy, and when the thermal energy accumulates to a certain extent, it will produce biological effects; the cavitation effect is similar to the microbubble principle of shock waves. When ultrasound passes through a liquid medium, it will produce a nearly vacuum cavity, and when the cavity collapses, it releases energy to stimulate the surrounding tissue cells;
As a mechanical vibration, ultrasound can not only cause the temperature of the medium to rise when it passes through the medium, but also cause the mechanical movement of the medium. Similarly, acting on human cells can also cause mechanical vibrations in the cells, and mechanical movement of appropriate intensity can cause changes in cell metabolism but not cause cell breakage. Ultrasound can be divided into high-intensity ultrasound (>3W/cm2) and low-intensity ultrasound (<3W/cm2) according to the sound wave energy density. According to the ultrasound type, it can be divided into continuous ultrasound and pulsed ultrasound.
LIPUS, as a low-intensity ultrasound, outputs energy in the form of pulses. It has been widely used in rehabilitation medicine, pain relief, fracture repair, chronic prostatitis and other fields. In clinical and research work, the operating frequency of LIPUS probe is usually 1~3MHz, the ultrasound intensity is between 0.03-1.00W/cm2, and the pulse ratio is 1:4 (that is, 200μs ultrasound time plus 800μs test time form a set of cycles)